Why is governance important?
Governance is important because it lays down a foundation to have a balance between transformation and risk mitigation such as maintaining compliance, creating cost visibility and control, improving security posture etc.
Here are some questions that should be asked regarding governance:
- Who is responsible for monitoring, support, and operations?
- Which services should be migrated to Azure?
- What roles & responsibilities must be defined?
- What security measures should we consider?
- What are the core processes needed
for service management? - How do we ensure a balance between innovation,
cost and agility? - What organizational changes are needed?
- What key capabilities must be developed?
- Azure governance building blocks?
Governance benchmark assessment
aka.ms/adopt/assess/govern
Understand business risk

Here are some questions that should be asked when defining corporate policy:
- What are your compliance requirements?
- Have you identified your business risks as it relates to cloud?
- What are your business priorities and reasons for moving to cloud?
- How do you think about data risks and data governance?
- Is there a list of applications which are prioritized by business impact?
- Do you have specific application governance requirements?
- How do you audit for compliance?
governance pillars

Establish controls and processes to ensure proper allocation of cost across business units.
Define cost management Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) model.
Establish policies to protect network, assets and data on your Azure environment.
Implement the foundation for governance best practices with appropriate resource organization.
Define the appropriate Azure management groups and subscriptions model to reflect security, operations and business hierarchy.
Protect your data and assets in the cloud by implementing identity and access control.
Define Azure RBAC model; using RBAC segregate duties within a team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their job.
Operationalize Azure Privileged Identity Management (PIM) as cloud based identity is an iterative process.
Establish polices to govern asset configuration or deployments, which could be manual or automated through DevOps best practices.
The DevOps practices in this discipline include:
Infrastructure as code
- Stand up environments in the fastest means possible.
- Remove the human element and reliably and repeatable deploy every time.
- Improve environment visibility and improve developer efficiency
- Store infrastructure definitions alongside application code.
Continuous integration and continuous deployment
- Accelerate delivery through automation
- Simple and easy to use
- Global community for actions
GOVERNANCE WITH AZURE NATIVE TOOLS
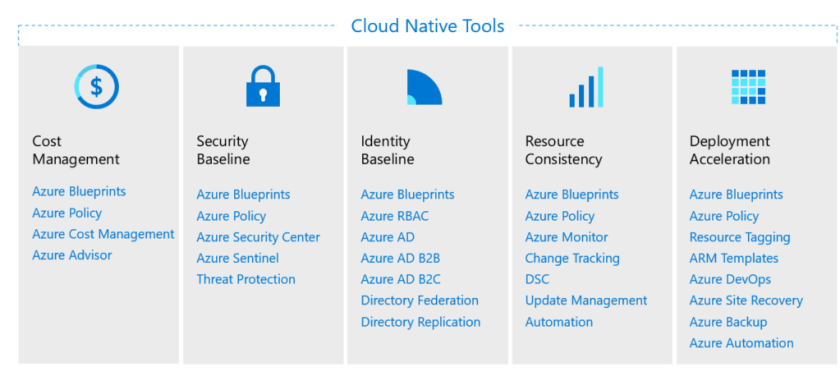
Governance Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
The below diagram illustrates the governance MVP and three governance iterations. Since these are iterations process, the process will evolve with each workload and maturity of the cloud.

Build the governance MVP
| Standard enterprise | Complex enterprise |
| 1. Customers or staff reside largely in one geography | 1. Customers or staff reside in multiple geographies or require sovereign clouds |
| 2. Business units share a common IT infrastructure | 2. Multiple business units that do not share a common IT infrastructure |
| 3. Single IT budget | 3. Budget allocated across business units and currencies |
| 4. Capital expense-driven investments are planned yearly and usually cover only basic maintenance | 4. Capital expense-driven investments are planned yearly; often include maintenance and refresh cycles of 3-5 years |
| 5. Datacenter or third-party hosting providers with fewer than five datacenters | 5. Datacenter or third-party hosting providers with more than five datacenters |
| 6. Networking includes no WAN; or 1-2 WAN providers | 6. Networking includes complex network or global WAN |
| 7. Identity is a single forest, single domain | 7.Identity consists of multiple forests, multiple domains |
| 8. Cost Management (cloud accounting) showback model – billing is centralized through IT | 8. Cost Management (cloud accounting) chargeback model – billing can be distributed through IT procurement |
| 9. Security Baseline – protected data: company financial data and IP. Limited customer data. No third-party compliance requirements. | 9. Security Baseline (protected data) – Multiple collections of customers’ financial and personal data |
This wraps up the Cloud Adoption Framework – Governance Overview.